DIY Image AI on ESP32-S3: Easier Than You Think
Forget complex setups. A new report shows you can train powerful image classification models for an ESP32-S3 microcontroller in just five minutes. Seriously.
What’s Happening
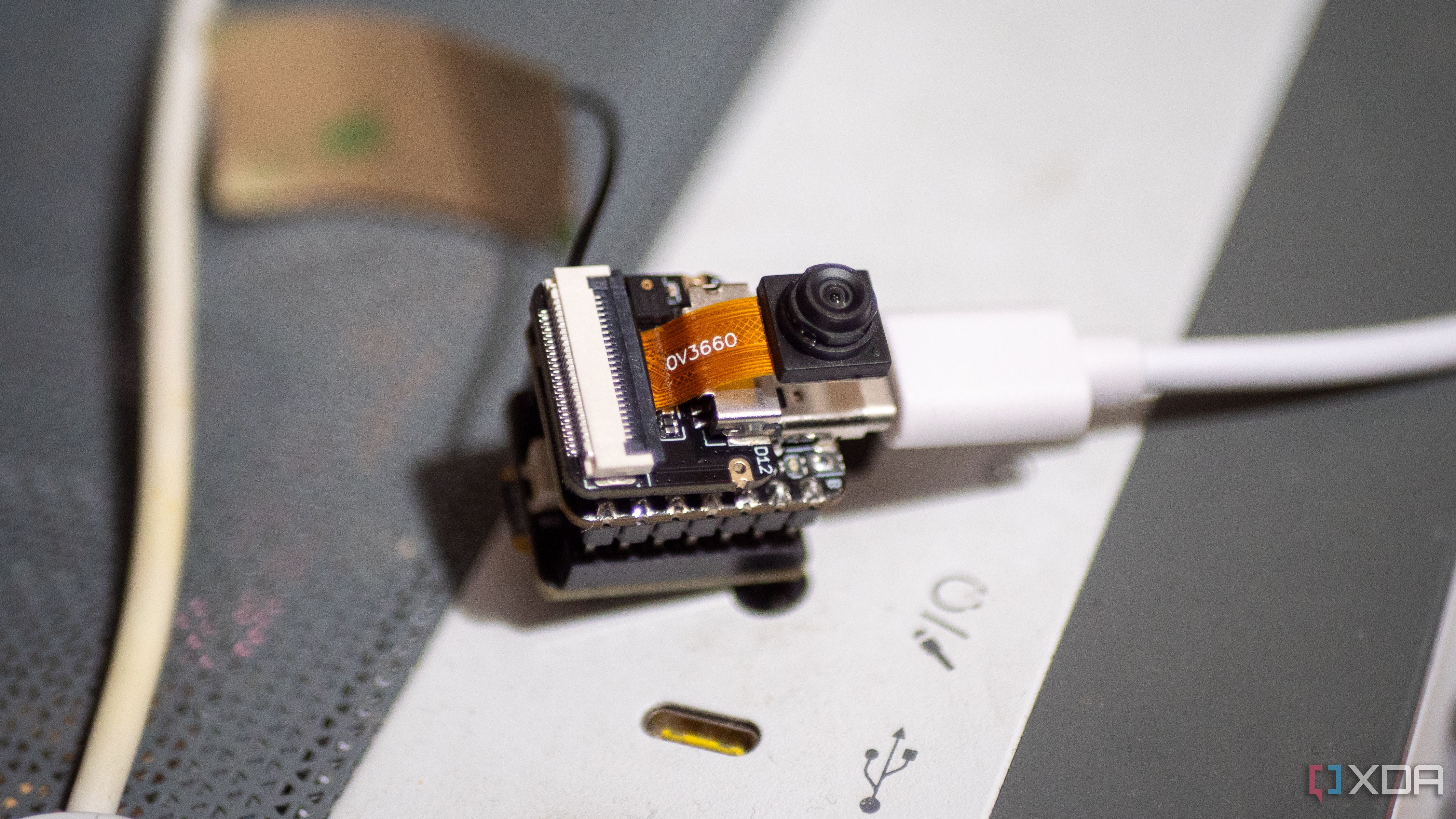
A recent report has ignited significant excitement within the tech community, showcasing how surprisingly straightforward it is to develop custom image classification models for the ESP32-S3 microcontroller. One innovative enthusiast even claims to have accomplished this impressive feat in an astonishing five minutes.
This development challenges the long-held perception that deploying sophisticated artificial intelligence on low-cost, embedded hardware demands extensive expertise and considerable time. It firmly points towards a new, more accessible era of AI development for everyone, from seasoned engineers to curious hobbyists.
The ESP32-S3, known for its powerful dual-core processor and integrated AI acceleration capabilities, is rapidly proving itself as a true game-changer in the embedded world. It’s no longer confined to basic IoT tasks but now stands as a remarkably viable platform for cutting-edge, on-device machine learning at lightning speed.
Why This Matters
This breakthrough fundamentally democratizes access to powerful AI tools, effectively moving them out of specialized research labs and directly into the hands of everyday developers and makers. Imagine the expansive possibilities for creating truly smart, autonomous devices that operate without constant reliance on cloud connectivity.
Consider building a smart security camera capable of identifying specific pets or individuals entirely locally, ensuring sensitive data never leaves your home network. Or envision an intelligent garden system that precisely detects plant diseases or pests in real-time, all powered by an inexpensive, tiny chip.
Traditionally, integrating custom AI models into compact embedded systems was often a complex, multi-stage process, typically involving highly specialized frameworks and significant computational resources. The reported ease of training and deployment on the ESP32-S3 dramatically lowers this barrier, making advanced AI practical for smaller projects.
This pivotal shift means accelerated prototyping cycles, substantially reduced development costs, and the capability to craft more private, responsive, and strong AI applications. It represents a significant leap forward for edge computing, bringing genuine intelligence much closer to the source of the data itself.
-
Rapid Innovation: Developers can now quickly iterate, test, and refine AI concepts directly on their target hardware.
-
Enhanced Privacy: Critical image analysis can occur entirely locally, ensuring sensitive personal data remains off the cloud.
-
Offline Functionality: Devices gain the ability to operate intelligently and autonomously even without any internet connection.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Advanced AI capabilities are now achievable by leveraging inexpensive, widely available hardware like the ESP32-S3.
The Bottom Line
The ability to train and successfully deploy complex image classification models on an ESP32-S3 in mere minutes signifies a profound and exciting shift in the landscape of embedded artificial intelligence. It transforms what was once considered a niche, expert-level skill into a widely accessible and practical capability.
This remarkable ease of entry means we can confidently anticipate a surge in innovative, AI-powered gadgets and IoT solutions across an incredibly diverse range of sectors, from smart homes and personal wearables to sophisticated industrial automation. The future of intelligent devices is rapidly becoming more personal, pervasive, and incredibly innovative.
Is this the pivotal moment when custom, powerful AI becomes a standard, expected feature for every tinkerer, small business, and product developer, fundamentally changing how we interact with and build technology?
Originally reported by XDA Developers
Got a question about this? 🤔
Ask anything about this article and get an instant answer.
Answers are AI-generated based on the article content.
vibe check:
