LLMs Output Text, Not Data: Pydantic's Validation Fix
LLMs are great for text, but terrible for structured data. Learn how to tame their outputs for reliable, actionable information.
✍️
main character energy 💫 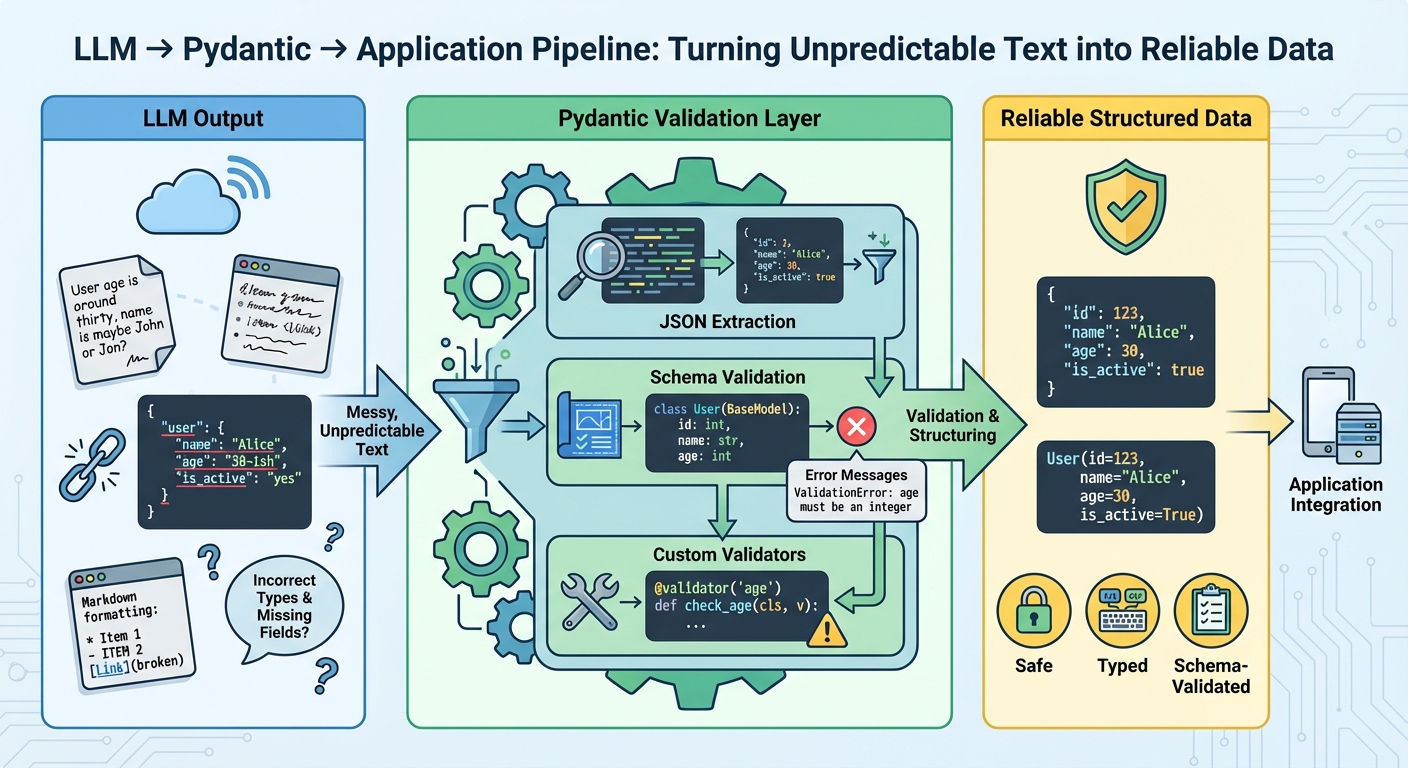
What’s Happening Here’s a crucial fact many overlook: large language models fundamentally generate text. Their training data consists of vast amounts of human language, so their natural output format is free-form, conversational prose, not neatly organized structured data. This creates a significant challenge for developers. Even when you explicitly prompt an LLM to return data in a specific format like JSON, it’s not guaranteed to comply perfectly. A missing comma, an extra comment, or an incorrect data type can easily break your downstream parsing logic. ## Why This Matters Building applications that rely on LLMs for structured information — like extracting customer details or product specifications — becomes a headache without a strong validation layer. Imagine your system expecting a price as a float, but the LLM sometimes outputs it as a string, or worse, includes currency symbols. Such inconsistencies are not just annoying; they’re critical blockers for production-grade applications. Every manual intervention to clean data or debug broken parsers wastes valuable development time and introduces potential errors. This is precisely where tools like Pydantic become indispensable. Pydantic, a Python library, allows you to declaratively define the exact data schema you expect from an LLM. You create Python classes representing your desired structure, and Pydantic then attempts to parse the LLM’s text output into that format, raising clear, actionable errors if the structure or types don’t match. Here’s why this approach is a game-changer:
- Guaranteed Data Integrity: Ensures LLM outputs conform to predefined schemas, preventing malformed data from entering your systems.
- Automated Error Handling: Pydantic provides detailed validation errors, simplifying debugging and allowing for programmatic error recovery or re-prompting.
- Reduced Developer Overhead: Eliminates the need for custom, brittle parsing logic and extensive manual checks, freeing up engineering time.
- Enhanced System Reliability: Builds trust in LLM-powered features by ensuring predictable and consistent data flows.
- smooth Integration: Makes LLM outputs compatible with existing structured data pipelines, databases, and APIs with minimal effort.
- Improved Scalability: Allows applications to process LLM outputs at scale without constant human intervention for data cleanup. ## The Bottom Line While large language models are revolutionizing text generation, their inherent textual nature demands a strategic approach for use cases requiring structured data. Pydantic acts as a crucial bridge, transforming raw, often flaky LLM text into dependable, validated data, which is absolutely essential for strong AI applications. How critical will such validation layers become as LLMs integrate further into our data-driven systems?
✨
Originally reported by ML Mastery
Got a question about this? 🤔
Ask anything about this article and get an instant answer.
Answers are AI-generated based on the article content.
vibe check: